Cross Cutting Examples Geology Steno s law or principle of cross cutting relationships states that a rock body or geological feature that disrupts cuts or deforms another is younger
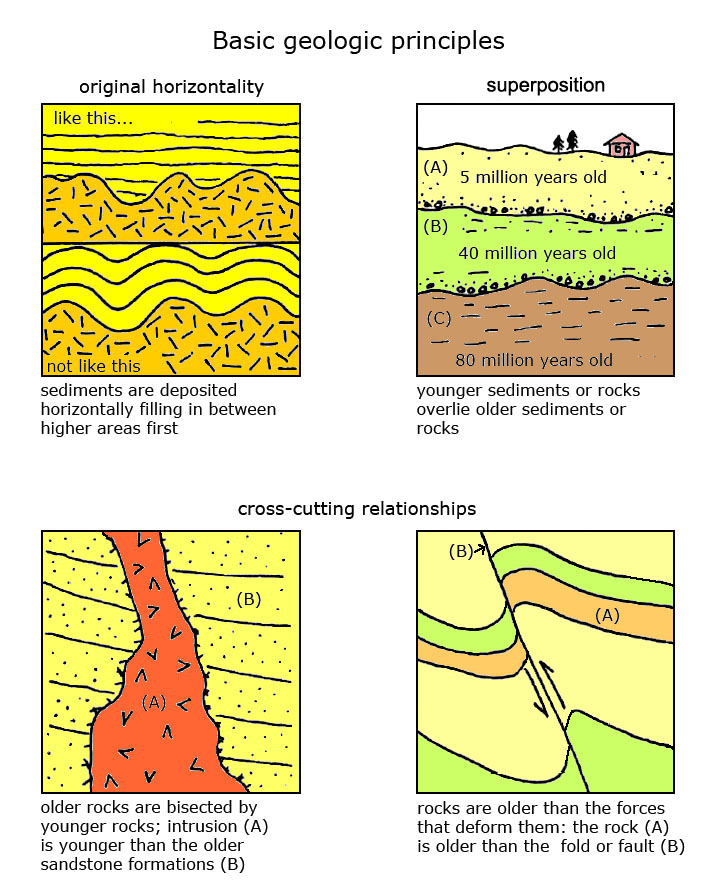
James Hutton s observations related to uniformitarianism also serve as the basis for another important geologic principle called cross cutting relationships which is a technique used in relative age dating In short an intrusive rock body is younger than the rocks it intrudes For example Salisbury Crag a prominent Edinburgh landmark known to Hutton owes its relief to a thick sheet of The principle of cross cutting relationships may be stated as follows when one geological feature cuts through another the former is the younger and the latter is the older of the two features Cross cutting relationships For example consider the diagram to the right The brown sedimentary rocks A must be older than the dike B that cuts through the strata the dike must be older than
Cross Cutting Examples Geology
 Cross Cutting Examples Geology
Cross Cutting Examples Geology
https://image1.slideserve.com/1774123/cross-cutting-relationships-l.jpg
Instructions You will be determining the relative order in which geological events occurred as shown in this generic stratigraphic cross section below Stratigraphy is the study of the rock strata or layers and is usually applied to sedimentary and sometimes volcanic rocks Figure 3 Diagram illustrating cross cutting relations in geology
Templates are pre-designed files or files that can be utilized for various functions. They can save effort and time by offering a ready-made format and layout for creating different type of material. Templates can be used for individual or professional projects, such as resumes, invitations, leaflets, newsletters, reports, presentations, and more.
Cross Cutting Examples Geology
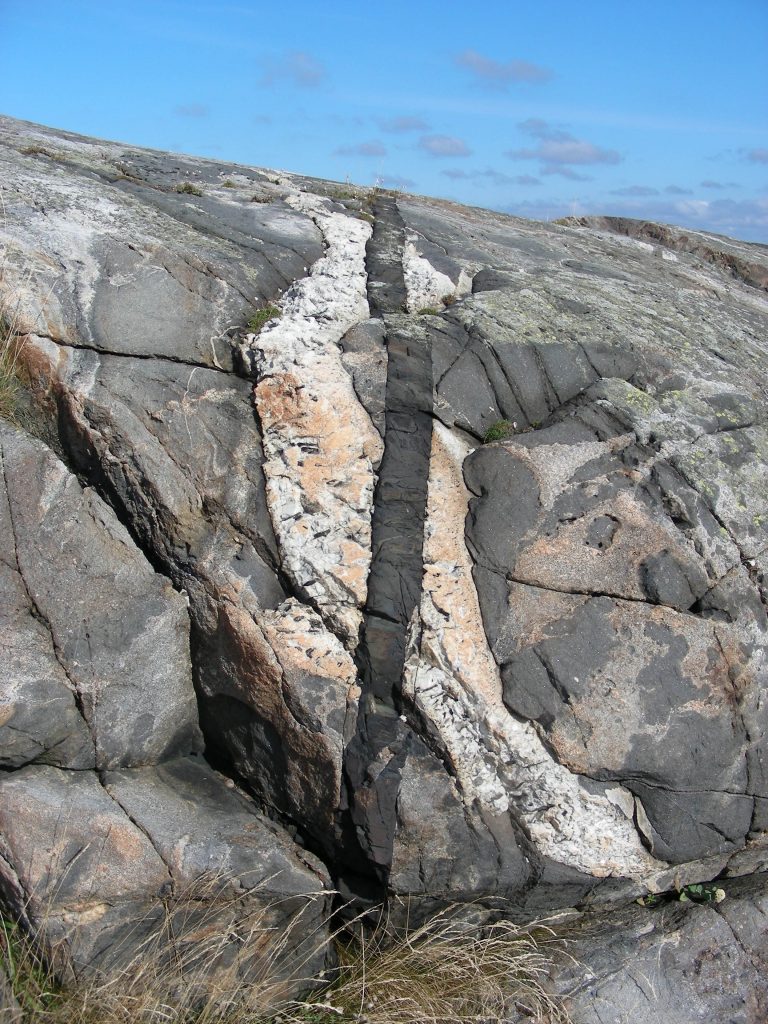

Cross cutting Relationships Polarpedia
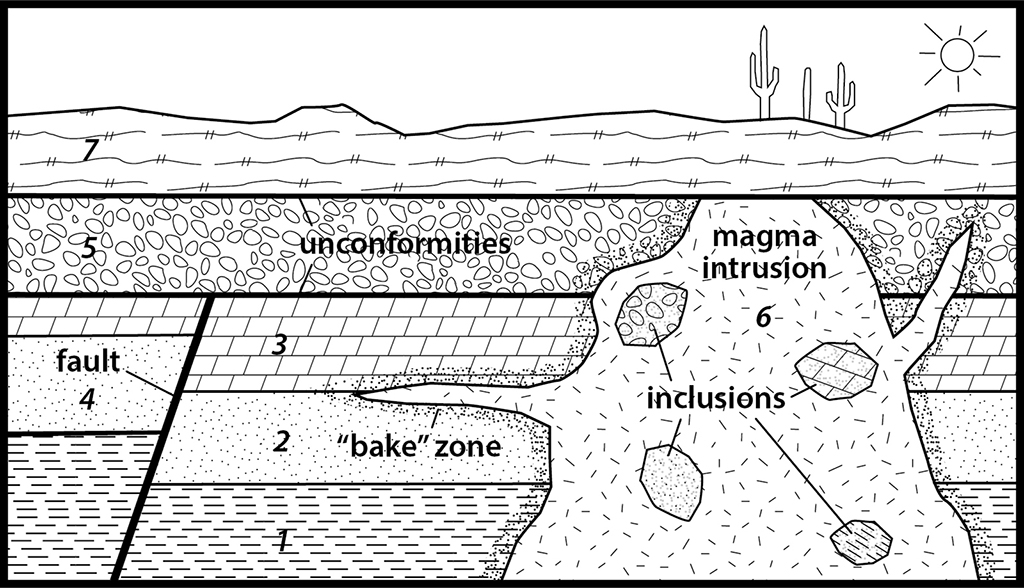
Law Or Principle Of Inclusions State In Geology Explained Geology Base

Law Of Superposition And Relative Dating Of Rocks Geology

Pin On Geology
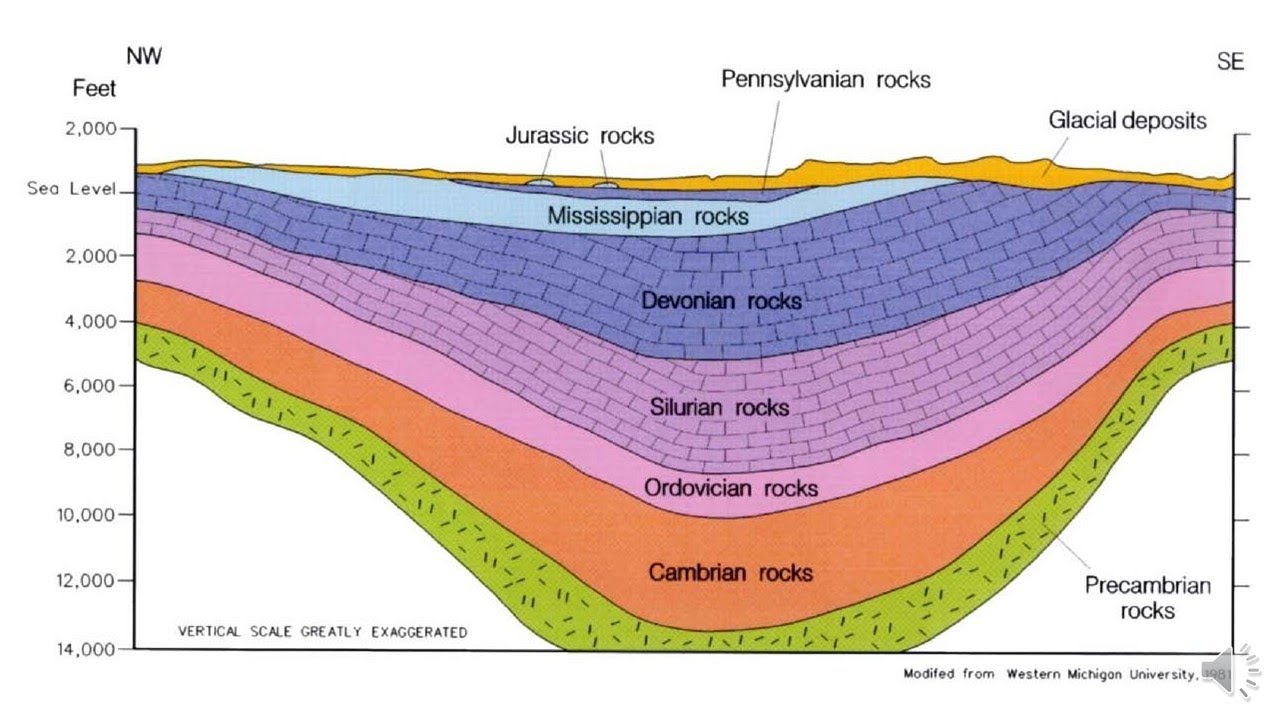
Cross Section Geology
1 42 Radiocarbon Dating And Relative Dating Geosciences LibreTexts

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cross-cutting_relationships
Cross cutting relationships is a principle of geology that states that the geologic feature which cuts another is the younger of the two features It is a relative dating technique in geology
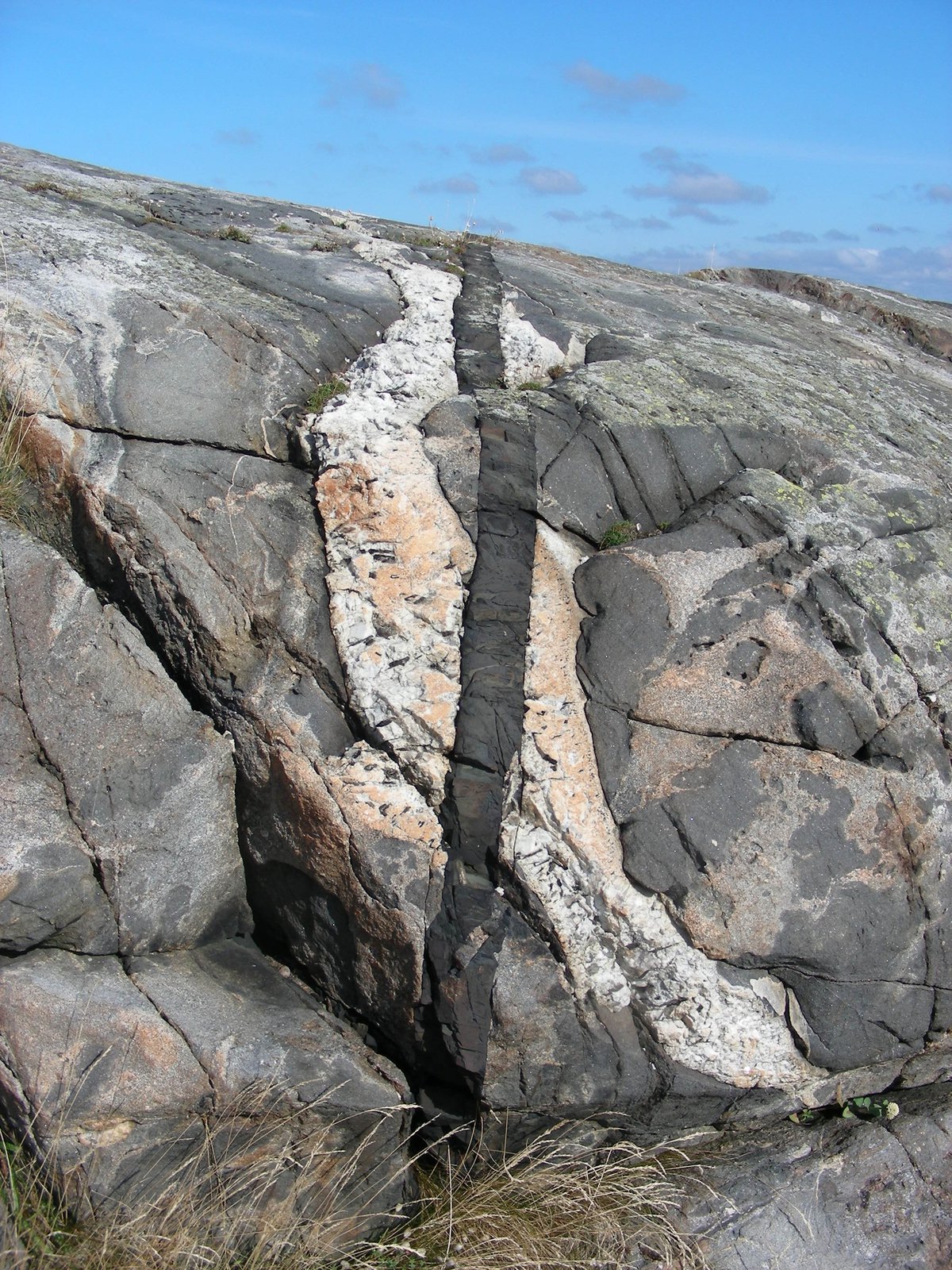

https://www.nps.gov/articles/geologic-principles-cross-cutting-relationships.htm
Cross cutting Relationships Intrusions In short an intrusive rock body is younger than the rocks it intrudes For example Salisbury Crag a prominent Edinburgh landmark known to Hutton owes its relief to a thick sheet of resistant basalt Hutton showed from the super heated contacts below and above and from places where the basalt actually invaded underlying and overlying beds that the
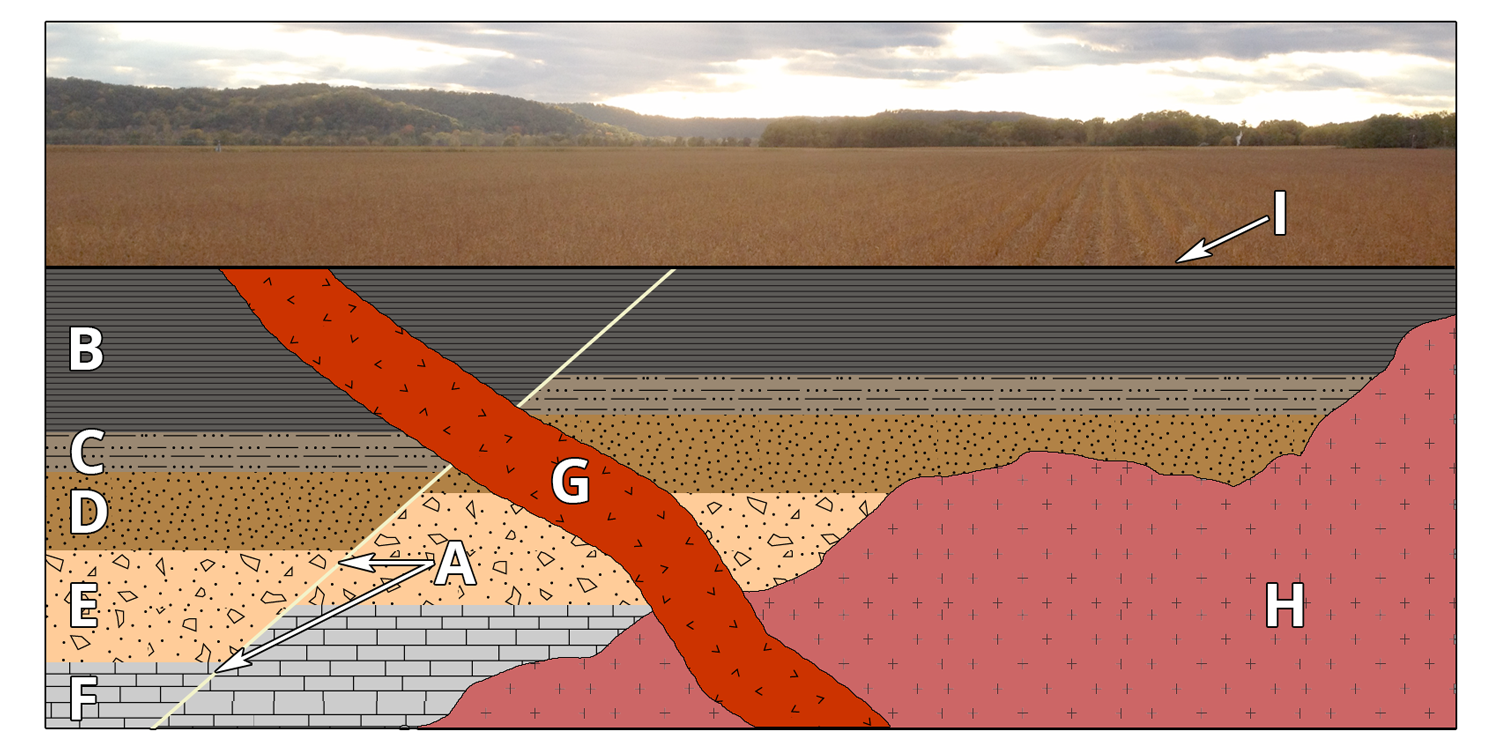
https://www.geologyin.com/2023/05/cross-cutting-relationships.html
Cross cutting relationships can be used to determine the relative ages of rock strata and other geological structures They are one of the basic principles of geology that is used to understand the history of the Earth

https://geo.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Geology/Introduction_to_Historical_Geology_(Johnson_et_al.)/09%3A_Geologic_Time_and_Relative_Dating/9.02%3A_Original_Horizontality_and_Cross-Cutting_Relationships
Cross cutting relationships may be compound in nature For example if an unconformity truncated a fault and that unconformity was cut by a dike Based upon such compound cross cutting relationships it can be seen that the fault is older than the unconformity which in turn is older than the dike

https://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/fossils/laws.html
Numeric ages from the flow and dike and relative ages from the fossils in the surrounding rocks contribute to the geologic time scale The granite dike a mass of rock that cuts across the structure of the rocks around it shown here illustrates the Law of Cross Cutting Relations
[desc-11] [desc-12]
[desc-13]